Temperature Coefficient of Resistance
The temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) is one of the main used parameters to characterize a resistor.
This coefficient defines the change of the resistance as a function of temperature, and it is usually expressed in ppm/°C, which stands for parts per million per centigrade degree (1 ppm = 0.0001%). The temperature coefficient of resistance is calculated as follows:
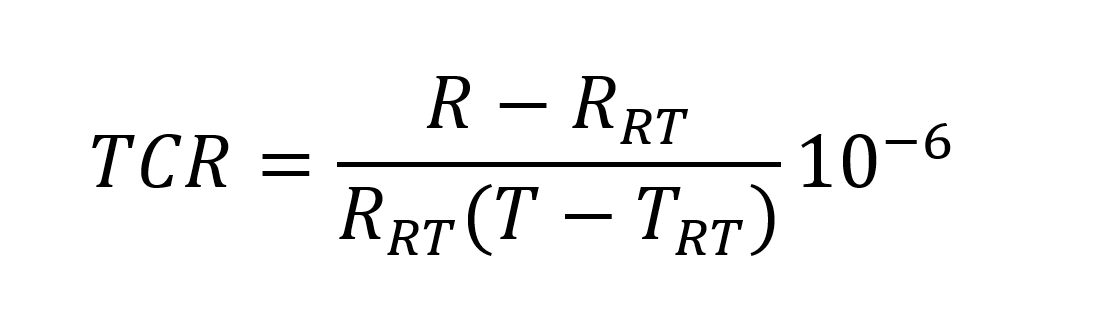
The TCR is in ppm/°C, RRT is the resistance at room temperature, R is the resistance at operating temperature, TRT is the room temperature (typically 25°C) and T is the operating temperature in °C.
The TCR is an important parameter that enables the end user to accurately predict the influence of temperature changes on the resistance value, and consequently the potential of creating measurement uncertainty.
In many cases, resistor manufacturers do not provide enough information to enable an end user to accurately predict the influence of temperature. For instance, they provide a TCR value but do not indicate the temperature range.
In applications where high-precision resistor performance and temperature stability are absolute requirements, the user must trust the TCR specification. The uncertainty is created when the TCR is calculated without enough data to allow the accurate prediction of the true impact of temperature change on the resistor performance.
TCR measuring
The TCR for a resistor is determined by measuring the resistances values over an appropriate temperature range. For linear behavior, the TCR is calculated through the average slope of the resistance value over a temperature interval. However, many materials have a non-linear coefficient, meaning it is very important to specify the TCR, as well as the temperature interval.
The way to measure TCR is standardized in MIL-STD-202 Method 304 – Resistance-temperature characteristic – where it is calculated for ranges between −55°C and 25°C, and between 25°C and 125°C (test temperature).
Resistors can have a negative, positive, or stable TCR over a certain temperature range.
Choosing the right resistor could prevent the need for temperature compensation.
Thermistors have a higher TCR
In some applications, it is desired to have a large TCR to measure temperature. Resistors used in these applications are known as thermistors, which are temperature sensors that vary the resistance of the semiconductor element according to the temperature to which they are exposed.
Typically, thermistors have a high TCR which gives them a high sensitivity, causing great resistance variations for small temperature variations.
We must also consider that there are two types of thermistors:
- NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient) - thermistors with a negative TCR: resistance decreases with increasing temperature.
- PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) - thermistors with a positive TCR: resistance increases with increasing temperature.
In the table below, we can observe an example of the temperature coefficient of resistance at 20°C, for a wide variety of materials.
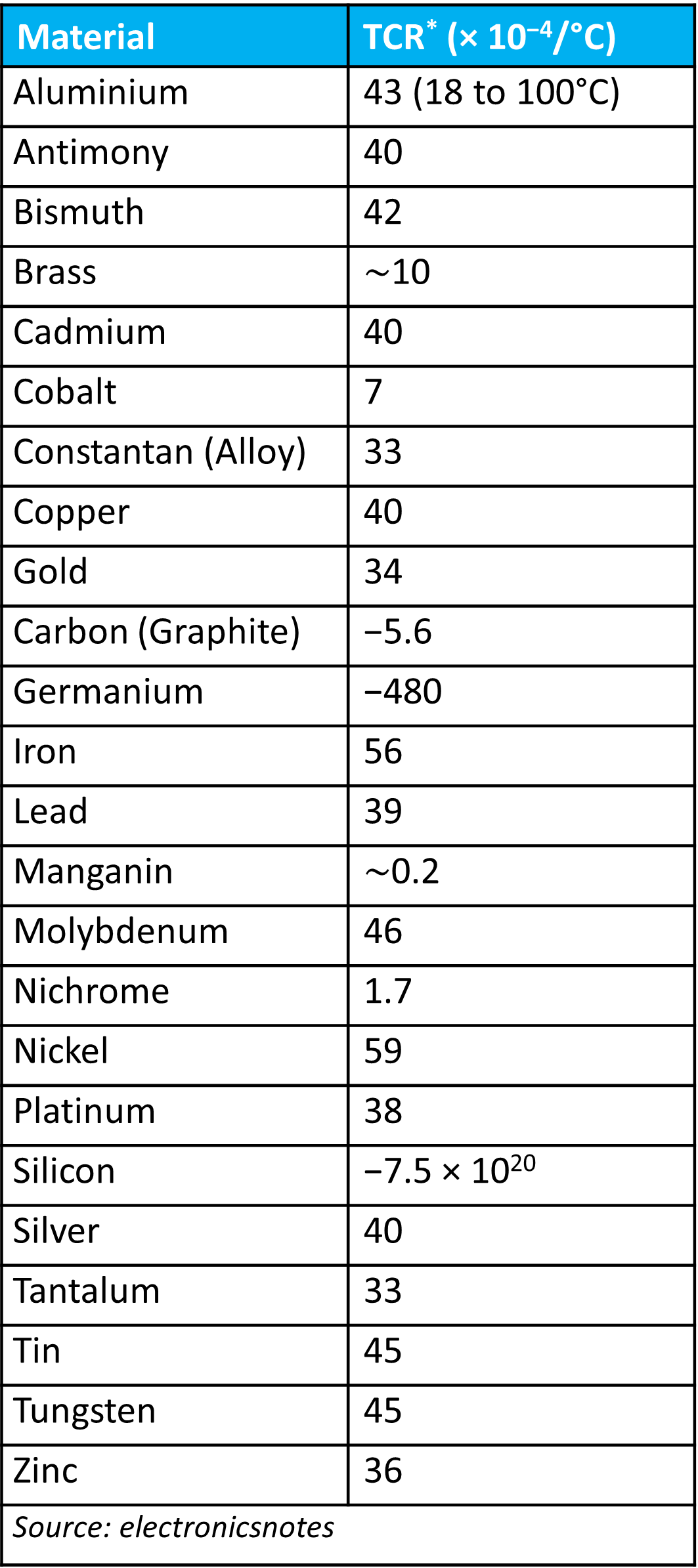
*Values for TCR depend on purity and temperature.
Tekon develops solutions for your industry
Tekon’s probes specialized department develops thermistors temperature solutions in for a wide range of industries and provides the best technical support for all clients.
Would you like to know more about compatible thermocouple head transmitters?
Contact us!
sales@tekonelectronics.com
+351 93 30 33 250